[ 문제 ] : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1504
1504번: 특정한 최단 경로
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 E가 주어진다. (2 ≤ N ≤ 800, 0 ≤ E ≤ 200,000) 둘째 줄부터 E개의 줄에 걸쳐서 세 개의 정수 a, b, c가 주어지는데, a번 정점에서 b번 정점까지 양방향 길이 존
www.acmicpc.net
[ 문제 접근 ]
코딩 테스트에서 다익스트라 문제가 나왔는데 가물가물한게 풀이법이 기억이 안났었다.
내가 애매하게 알고있었구나 를 느끼고 최단경로 문제들 싹 돌려 보려고 한다.
이 문제는 다익스트라 알고리즘에 특정 노드를 반드시 거쳐 가야하는 문제이다.
처음에 어떻게 구현 할까 고민하다가
1번 부터 시작해서 어떤 X, Y를 반드시 지난다는 것은,
1 -> X -> Y -> N
or 이 둘 중에 작은 값이 될 것이다.
1-> Y -> X -> N
여기까지는 생각 했는데 구현에서 막혀서 결국 못풀었다.
[ 처음 코드 ]
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using std::cin; using std::cout;
using std::vector;
int n, e;
const int INF = 987654321;
int d[801][801];
int path[801];
vector<std::pair<int, int>> graph[801];
struct cmp {
bool operator()(std::pair<int,int> a, std::pair<int,int> b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
};
void dijkstra(int start,int x) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>,vector<std::pair<int,int>>,cmp> que;
d[start][start] = 0;
que.push({ start,0 });
while(!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.top().first;
int cur_d = que.top().second;
que.pop();
if (cur == x) return;
if (d[start][cur] < cur_d) continue;
for (size_t i = 0; i < graph[cur].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[cur][i].first;
int next_d = graph[cur][i].second;
if (d[start][next] > d[start][cur] + next_d) {
d[start][next] = d[start][cur] + next_d;
que.push({ next,d[start][next] });
}
}
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> e;
while (e--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
graph[a].push_back({ b,c });
graph[b].push_back({ a,c });
}
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
std::fill_n(d[i] + 1, n, INF);
}
long long sum = 0; // 1 -> X -> Y -> N 서로 하나도 연결 안되어있어서
// INF + INF + INF 가 될 수 도 있어서 long long
dijkstra(1, n);
dijkstra(x, n);
dijkstra(y, n);
// 1 -> X -> Y -> N // 1 -> Y -> X -> N
sum = std::min(d[1][x] + d[x][y] + d[y][n], d[1][y] + d[y][x] + d[x][n]);
if (sum >= INF) sum = -1;
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
어디가 문제 인지 몰라서 결국 구글링.
성공한 코드를 보니 나랑 비슷하게 풀었는데 왜 내껀 안되는지.. 맞왜틀 발동.]
[ 성공한 다른 사람 코드 ]
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define VMAX 801
#define INF 2100000000
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int,int>> a[VMAX];
bool pass = true;
int dijkstras(int start, int end){
priority_queue<pair<int,int>> pq;
int dist[VMAX];
for(int i=1; i<VMAX; i++)
dist[i] = INF;
dist[start]=0;
pq.push({-0, start});
while(!pq.empty()){
int x = pq.top().second;
int wx = -pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
if(x==end) return wx;
for(int i=0; i<a[x].size(); i++){
int y = a[x][i].first;
int wy = a[x][i].second;
if(dist[y] > dist[x] + wy){
dist[y] = dist[x] + wy;
pq.push({-dist[y], y});
}
}
}
pass = false;
return 0;
}
int main(){
int n,e; cin >> n >> e;
int v1, v2;
for(int x,y,w,i=0; i<e; i++){
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &w);
a[x].push_back({y,w});
a[y].push_back({x,w});
}
cin >> v1 >> v2;
int num1 = dijkstras(1, v1) + dijkstras(v1, v2) + dijkstras(v2, n);
int num2 = dijkstras(1, v2) + dijkstras(v2, v1) + dijkstras(v1, n);
int result = min(num1, num2);
if(pass)
printf("%d\n", result);
else
printf("-1\n");
}cf ) 참고로 바로 위의 코드는 dikstra를 6번 해줬는데 원하는 d[] 값을 아려면 사실 6번 까지 필요 없다. ( 시간 초과가 날 수 도 있다. )
차이를 보니 다익스트라 while 문 안에서 나는 cur == n 일때 return 하고 종료되게끔 했는데
위의 코드는 cur != n 이라 return 하지 않고 while문이 끝나게 되면 flag를 false로 설정해서 마지막 정답 출력 할때 사용하였다.
이게 무슨 의미 일까?
그래프가 단절된 경우를 찾아낸다.
dijkstra( 1 , n ) 하면 1부터 2,3,4... n 까지의 최단 경로를 구하다가 현재 priority_queue에서 나온 노드가 n 일때
if 문에 걸리게 된다. 이 말은 현재 노드가 내가 찾고자 하는 노드 일때 라는 의미.
근데 dijkstra( 1 , n ) 했는데 중간에 if문에 걸려서 return 되지 않고 함수를 다 돌고 종료가 됐다면 1 to n 까지 가는 길이 없다는 소리이다. ( 이 경우는 INF 로 초기화 되어있다. )
즉, 그래프가 끊어졌다고 판단하는것이다. 그리고 그 판단을 bool 변수로 체크해준다.
false 라면 최단경로 탐색 불가능 -> -1
true 라면 최단경로 탐색 완료 -> result
를 출력한다.
그런데 여기서 중요한 점 한가지가 더 있다.
while 문 안에서
if (cur == x) return;
가 있으면 예상치 못한일이 벌어 질 수 있다.
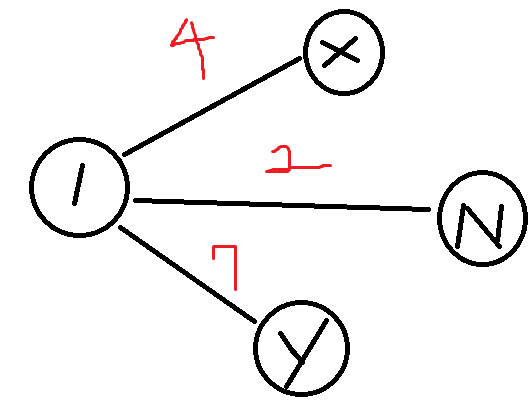
현재 1번 노드라고 하자. 그리고 1번 노드에서 시작해서 다른 모든 노드까지의 거리인 d[] 를 알고 싶어
dijsktra(1,n)을 했다고 한다면 어떻게 될까?
1번 노드의 다음 노드로는 가장 작은 엣지인 2를 가진 N을 선택할 것이다.
이때 N을 선택하게 되면 if문을 만나 return 되고 다익스트라 함수가 종료되는것이다.
그럼 이 때 X와 Y의 d[X] d[Y] 값은 계산이 안된 채로 종료되고, 계산이 되지 않았으면 초기화 값인 INF 를 가지게 된다.
그렇게 된다면 dijkstra(1,n) 을 통해서 d[1][x] ( 1부터 X까지 거리 ) 와 d[1][y] ( 1부터 Y까지의 거리) 가 각각 4,7 인데도 불구하고 서로 연결되어 있지 않는 INF 값을 가지게 되는 것이다.
즉, dijkstra(1,n) 을 했을때 d[1][x] , d[1][y] 를 구한다는 보장이 없다.
이러한 문제로 if (cur == x) return; 를 지우게 되면 성공하는것을 알 수 있다.

근데 이렇게 되면 사실 효율이 조금 떨어지는게 사실이다. 아무래도 전부 도니깐 말이다.
그럼 if (cur == x) return; 쓰면서 맞출 수 있는 방법이 있을까?
std::min ( dijkstras(1,x) + dijkstras(x, y) + dijkstras(y, n),
dijkstras(1, y) + dijkstras(y, x) + dijkstras(x, n) );
dijstra(1,n) 이 아니라 dijstra(1, x) 를 실행시켜 함수가 진행되는 동안 d[x] 값을 구하는 것을 보장해주면 된다.
....
근데 사실 이렇게 되면 dijkstra 알고리즘을 6번 사용 하게 되니깐 더 비효율적이긴 하다.
이것도 싫다면,
https://yabmoons.tistory.com/386
얌문s 블로그에 나와있는것 처럼 dijkstra 4번과 flag를 이용해서 푸는 방법이 있다.
[ 최종 코드 ver.1]
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using std::cin; using std::cout;
using std::vector;
int n, e;
const int INF = 987654321;
long long d[801][801]; // INF가 더해지면 int 로는 부족하다.
int path[801];
vector<std::pair<int, int>> graph[801];
struct cmp {
bool operator()(std::pair<int, int> a, std::pair<int, int> b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
};
void dijkstra(int start, int x) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>, vector<std::pair<int, int>>, cmp> que;
d[start][start] = 0;
que.push({ start,0 });
while (!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.top().first;
int cur_d = que.top().second;
que.pop();
// if (cur == x) return; dijkstra(1,n) 을 했을때 d[1][x] , d[1][y] 를 구한다는 보장이 없다.
if (d[start][cur] < cur_d) continue;
for (size_t i = 0; i < graph[cur].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[cur][i].first;
int next_d = graph[cur][i].second;
if (d[start][next] > d[start][cur] + next_d) {
d[start][next] = d[start][cur] + next_d;
que.push({ next,d[start][next] });
}
}
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> e;
while (e--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
graph[a].push_back({ b,c });
graph[b].push_back({ a,c });
}
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
std::fill_n(d[i] + 1, n, INF);
}
long long sum = 0; // 1 -> X -> Y -> N 서로 하나도 연결 안되어있어서
// INF + INF + INF 가 될 수 도 있어서 long long
dijkstra(1, n);
dijkstra(x, n);
dijkstra(y, n);
// 1 -> X -> Y -> N // 1 -> Y -> X -> N
int a = std::min(d[x][y], d[y][x]);
sum = std::min(d[1][x] + a + d[y][n], d[1][y] + a + d[x][n]);
if (sum >= INF) sum = -1;
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
[ 최종 코드 ver.2]
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using std::cin; using std::cout;
using std::vector;
int n, e;
const int INF = 987654321;
bool flag = true;
vector<std::pair<int, int>> graph[801];
struct cmp {
bool operator()(std::pair<int, int> a, std::pair<int, int> b) {
return a.second > b.second;
}
};
int dijkstra(int start, int x) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<int, int>, vector<std::pair<int, int>>, cmp> que;
int d[801];
std::fill_n(d + 1, n, INF);
d[start] = 0;
que.push({ start,0 });
while (!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.top().first;
int cur_d = que.top().second;
que.pop();
if (cur == x) return cur_d;
if (d[cur] < cur_d) continue;
for (size_t i = 0; i < graph[cur].size(); i++) {
int next = graph[cur][i].first;
int next_d = graph[cur][i].second;
if (d[next] > d[cur] + next_d) {
d[next] = d[cur] + next_d;
que.push({ next,d[next] });
}
}
}
flag = false; // 수정 후
return d[x];
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> e;
while (e--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
graph[a].push_back({ b,c });
graph[b].push_back({ a,c });
}
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
int a = dijkstra(1, y) + dijkstra(y, x) + dijkstra(x, n);
int b = dijkstra(1, x) + dijkstra(x, y) + dijkstra(y, n);
int sum = std::min(a, b);
if (flag) cout << sum;
else cout << -1;
return 0;
}위 코드에서 생각해볼 점은
d[] 배열을 long long 이 아닌 int 타입으로 해도 된다는 점과, d[] 배열을 전역 변수로 두지 않는다는 점이다.
[ Key Point ]
👉 d[1][x] , d[1][y] 는
dijkstra(1, n);한번의 다익스트라 함수로 알 수 있다.
👉 d[x][y] 는 d[y][x] 랑 같기 때문에 둘 중에 한번의 다익스트라 연산으로 계산 가능하다.
dijkstra(x, n);
dijkstra(y, n);
👉 주의할 점은 d[start][end] start 부터 end 까지 가는 비용을 저장하는 2차원 배열 d[][] 를 int 가 아닌 long long 으로 선언해주어야한다. 이것 때문에 어디서 틀린지 모르고 시간 많이 썼다..
[ 다른 사람 풀이 ]
ref :: https://chosh95.tistory.com/419
ref :: https://yabmoons.tistory.com/386
ref :: https://dmsvk01.tistory.com/85
'PS > BaekJoon' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [1780] 종이의 개수 - 재귀 / 분할 정복 ★★☆☆ / 복습 ○ (0) | 2021.12.02 |
|---|---|
| [10799] 쇠막대기 - 스택 ★★☆☆ / 복습 ○ (0) | 2021.11.30 |
| [5430] AC - 구현/문자열/덱 ★★☆☆ / 복습 ○ (0) | 2021.11.26 |
| [1021] 회전하는 큐 - 덱 ★☆☆☆ / 복습 ○ (0) | 2021.11.26 |
| [14719] 빗 물 - 스택/투 포인터/구현 ★★★☆ / 복습 ○ (0) | 2021.11.25 |